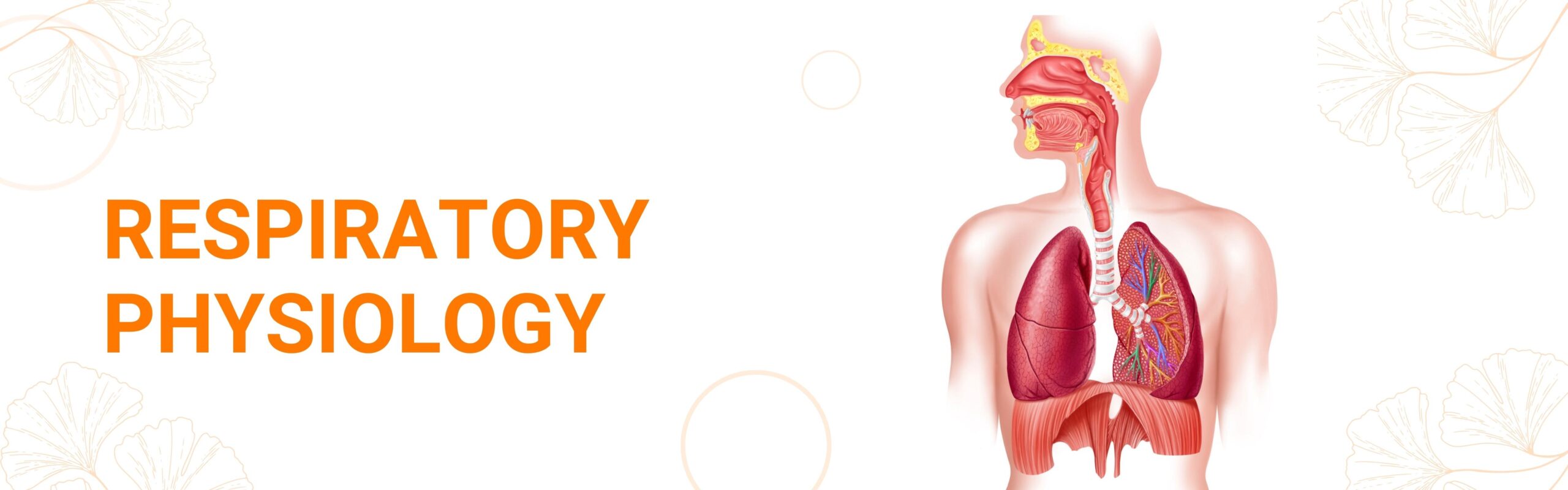
Respiratory physiology is the movement of oxygen from the outside environment to the cells and the transportation of carbon dioxide from the cells into the external environment. There are multiple processes involved in respiration: ventilation, external respiration, transportation, internal respiration, cellular respiration and exhalation.
Ventilation is the process of breathing in the air with the oxygen into the lungs.
External respiration is the process by which oxygen and carbon dioxide is exchanged in and out of the blood across the respiratory membranes (alveoli and capillaries) in the lungs.
Transportation is the process by which oxygen is transported into the tissues from the lungs and the carbon dioxide is transported from tissues to the lungs. Hemoglobin, an iron-containing protein in the red blood cells, plays a key role in this process. It binds the oxygen in it and carries it to the metabolizing tissues.
Internal respiration is the process by which oxygen and carbon dioxide is exchanged in and out of the blood across the respiratory membranes of the metabolizing tissues.
Cellular respiration is the process in which the oxygen delivered to the cells and the carbon dioxide is taken from the cells.
Exhalation is the process in which the carbon dioxide from the body is released into the external environment.
